🎉 Our new research SCALEL
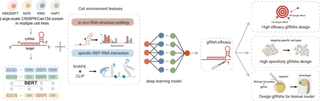 Image credit: SCALPEL
Image credit: SCALPEL🧬 SCALPEL: S͎pecific CRISPR-C͎as13d gRNA͎ design through deep L͎earning P͎rediction using in vivo E͎xperimentaL͎ RNA structure and binding information
📖 Abstract
The efficacy and tissue specificity of RNA therapeutics are critical for clinical translation. Here, by large-scale profiling of the dynamic RNA structurome across four cell lines, we systematically characterized the impact of in vivo target RNA structure and RNA-protein interactions on CRISPR/Cas13d gRNA activity. We identified the structural patterns of high-efficacy gRNA targets and observed that structural differences can lead to variations in efficacy across different cellular contexts. By stabilizing single-stranded structure, RNA-binding proteins also enhanced gRNA efficacy.
Leveraging this cell context information, along with approximately 290,000 RfxCas13d screening data, we developed SCALPEL, a deep learning model that predicts gRNA performance across various cellular environments. SCALPEL integrates:
- Both target and gRNA sequence
- In vivo icSHAPE data acorss different cell lines
- Cell type-specific RBP binding profiles
SCALPEL significantly outperforms existing models, and, most importantly, enables cell type-specific prediction of gRNA activity. Validation screens across multiple cell lines demonstrate that cellular context significantly influences gRNA performance, even for identical targeting sequences, underscoring the feasibility of cell type-specific knockdown by targeting structural dynamic regions. SCALPEL can also facilitate designing highly efficient virus-targeting gRNAs and gRNAs that robustly knockdown maternal transcripts essential for early zebrafish development. Our method offers a novel approach to develop context-specific gRNAs, with potential to advance tissue- or organ-specific RNA therapies.
🧠 Key Features
- 🧬 Integrating in vivo RNA secondary structure data and cell type-specific RBP binding profile
- 🧠 Transformer-based architecture for context modeling
- 🔁 Accurately predict on-target effects of gRNAs
- 🎯 Assist in designing high-specificity gRNAs for different cellular context
- 🔬 Facilitate the design of gRNAs for animal models
⚙️ Environment Setup && 🚀 Quick Start
Step 0: Download the pre-trained BERT model at Google Drive. Putting them in root directory.
Step 1: Prepare Input Data Like other_model_data/ours/demo_data.csv file. The icSHAPE sequencing data for all cell lines reported in this study have been deposited in the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) with accession number GSE301234. The validation screening sequencing data for all libraries are available in GEO under accession number GSE30081. These sequencing data have also been deposited in National Genomics Data Center (NGDC) the with accession number PRJCA042228.
- RNA sequences
- icSHAPE reactivity profiles
- RBP-binding tracks or matrices from PrismNet.
- Other features.
Step 2: Install python requirements in requirements.txt (Python3.9).
Step 3: Train SCALPEL.
- The
model_descan be configured to include sequence features along with any other features. - The
data_descan be configured ascell_line:{},match[i],random,target_genereferring to thetrain.shfile for specific usage. - It should be noted that you need to modify the paths that appear in the code, especially the
originpath in thecontrolfunction underlogicArchi.py. This path points to all the data files. According to our strategy, we perform different normalization for each gene based on all the data.
python3 -u logicArchi.py control --gpu_ids=[0] --model_des='seq_bert_fold_mfe1_mfe2_icshape_binding_relatelen_utrrate' --data_des='random' --model='SCALPEL' --dataset='BertOnehotLoader30' --lr=1e-3 --data_path='other_model_data/ours/demo_data.csv'
Step 4: Predict gRNA Efficacy referring to the val.sh file for specific usage.
python3 -u logicArchi.py val --gpu_ids=[0] --model_des='seq_bert_fold_mfe1_mfe2_icshape_binding_relatelen_utrrate' --data_des='random' --model='SCALPEL' --dataset='BertOnehotLoader30' --data_path={Your validation file path}
🙏 Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the following contributors and institutions for their support:
Collaborating Labs and Institutes
We thank all members in Sunlab at Shandong University for providing insightful discussions.Funding Support This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.32300521, No.32422013 and No.82341086); the Open Grant from the Pingyuan Laboratory (No.2023PY-OP-0104); the State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology Open Projects Fund (No.M2023-20; the Intramural Joint Program Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology (NO.SKLMTIJP-2024-02); the Double-First Class Initiative of Shandong University School of Life Sciences; the Young Innovation Team of Shandong Higher Education Institutions, the Taishan Scholars Youth Expert Program of Shandong Province, and the Program of Shandong University Qilu Young Scholars.
Open-source Tools
This project builds upon many open-source tools and libraries, including PyTorch, Scikit-learn, and Biopython.
Special thanks to all community members and beta testers who provided feedback during model development and validation in Sunlab.
📚 Related Publication
[1] Cheng, Xiaolong, et al. “Modeling CRISPR-Cas13d on-target and off-target effects using machine learning approaches.” Nature communications 14.1 (2023): 752.
[2] Wei, Jingyi, et al. “Deep learning and CRISPR-Cas13d ortholog discovery for optimized RNA targeting.” Cell Systems 14.12 (2023): 1087-1102.
[3] Wessels, Hans-Hermann, et al. “Prediction of on-target and off-target activity of CRISPR–Cas13d guide RNAs using deep learning.” Nature biotechnology 42.4 (2024): 628-637.
[4] Zhu, Haoran, et al. “Dynamic characterization and interpretation for protein-RNA interactions across diverse cellular conditions using HDRNet.” Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 6824.
[5] Yin, Weijie, et al. “Ernie-rna: An rna language model with structure-enhanced representations.” bioRxiv (2024): 2024-03.
🧾 Citation
If you use this work in your research, please cite:
@article{lu2025scalpel,
title={Deciphering Cellular Context for Efficient and Cell-Type Specific CRISPR-Cas13d gRNA Design using *in vivo* RNA structure and deep learning},
author={**},
journal={**},
year={2025},
note={**}
}
📄 License
This project is covered under the MIT License.
Thank you for using SCALPEL! Any questions, suggestions or advice are welcome!

